Isolation Techniques : A Comprehensive Guide
This article involves Comprehensive information on Isolation Techniques of microorganism, Its importance, Different Types, Factors affecting and Limitations.
Isolation Techniques : A Comprehensive Guide
Microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, are ubiquitous in nature and play crucial roles in various biological processes. To study these microorganisms in a laboratory setting, it is essential to isolate them from their natural environment. This process is known as isolation, and it involves separating a single species of microorganism from a mixture of different species. In this article, we will discuss various isolation techniques used in microbiology.
What is Isolation?
Isolation is the process of separating a single microorganism from a mixture of microorganisms. It involves obtaining a pure culture of microorganisms that can be studied and identified. Isolation techniques are necessary to study the characteristics of a single organism, such as its morphology, physiology, metabolism, and genetic makeup.
Why Isolation Technique is Important?
Isolation technique in microbiology is important for several reasons. First, it allows the study of individual microorganisms and their characteristics, such as morphology, physiology, and genetic makeup. Second, it is important for the identification of microbial pathogens that cause diseases. Third, isolation technique is essential for the production of pure cultures needed for the production of various biotechnological products.
Types of Isolation Techniques
There are several isolation techniques used in microbiology, and they are based on the physical and chemical properties of the microorganisms being studied. Some of the commonly used isolation techniques include:
Streak Plate Method
The streak plate method is a simple and commonly used isolation technique. It involves spreading a small amount of a mixture of microorganisms onto an agar plate and then streaking the mixture with a sterile inoculating loop. The loop is then sterilized and used to streak the plate again, and the process is repeated until individual colonies of microorganisms are visible.
Spread Plate Method
The spread plate method is similar to the streak plate method, but it involves spreading a known volume of a diluted mixture of microorganisms onto an agar plate using a sterile spreading tool. The microorganisms are then allowed to grow, and individual colonies can be isolated and studied.
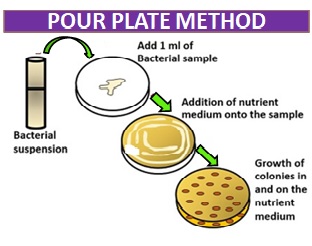
Pour Plate Method
The pour plate method involves mixing a known volume of a diluted mixture of microorganisms with liquefied agar and then pouring the mixture into a sterile petri dish. The agar is allowed to solidify, and individual colonies can be isolated and studied.
Serial Dilution method :
Serial dilution involves diluting a known volume of a mixture of microorganisms with a sterile diluent. The mixture is then serially diluted, and the diluted samples are spread or poured onto agar plates. The method allows for the isolation of individual colonies of microorganisms.
Filtration method
Filtration is a technique used to isolate microorganisms from liquids, such as water and food samples. The liquid is passed through a filter with a pore size small enough to retain the microorganisms. The filter is then placed onto an agar plate, and the microorganisms can be cultured and studied.
Enrichment Culture Method
The enrichment culture method involves providing a selective growth condition for the desired microorganism. This technique is particularly useful for isolating slow-growing or nutritionally fastidious microorganisms.
Immunological Methods
Immunological methods involve the use of antibodies to specifically detect and isolate microorganisms. These methods include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs)
Factors Affecting Isolation Technique
Several factors can affect the isolation technique in microbiology and they includes ,
1. Selection of Media
Different microorganisms have different nutritional requirements, and the selection of appropriate media is crucial for their isolation. The choice of media depends on the type of microorganism being isolated and its specific nutritional requirements.
2. Physical Factors
Physical factors, such as temperature, humidity, and light, oxygen can affect the growth and isolation of microorganisms. The optimal conditions for growth and isolation vary among different species of microorganisms.
3. Chemical Factors
Chemical factors, such as pH, nutrients, and inhibitors, can affect the growth and isolation of microorganisms. The type and concentration of nutrients and inhibitors in the culture medium can affect the isolation of microorganisms.
4. Biological Factors
Biological factors, such as competition and symbiosis, can affect the growth and isolation of microorganisms. The presence of other microorganisms in the culture medium can affect the isolation of the target microorganism.
What are the Advantage and Limitations of isolation Technique ?
Advantages : Isolation techniques in microbiology have advantages such as providing pure cultures for further study, allowing for identification, quantification, and characterization of microorganisms.
Limitations : Isolation Techniques in microbiology also have Limitations such as being selective and potentially biased, labor-intensive, and vulnerable to contamination.