Pour Plate Method – A Comprehensive Guide
Comprehensive guide on the pour plate method, including its principle, procedure, Troubleshooting, Quality Control, advantages, and Limitations.
What is mean by Pour Plate Method ?
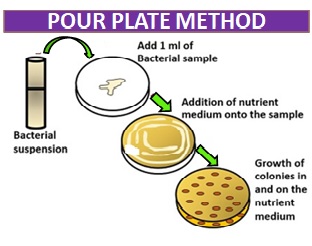
This method involves mixing a known volume of a diluted mixture of microorganisms with liquefied agar and then pouring the mixture into a sterile petri dish. The agar is allowed to solidify, and individual colonies can be isolated and studied.
Microbiological analysis plays a crucial role in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, food and medical diagnosis. One of the fundamental steps in microbiological analysis is the isolation and identification of microorganisms from the sample. This method is one of the most commonly used techniques for this purpose. It is a simple, inexpensive, and reliable method for the isolation and enumeration of bacteria.
Principle of Pour Plate Method
The principle of this method is based on the dilution of the sample by mixing it with a sterile liquefied agar medium. The diluted sample is then poured into a sterile Petri dish and allowed to solidify. As the agar solidifies, the bacteria in the sample become embedded in the agar. The colonies of bacteria then grow and develop on the surface and within the agar medium. This method allows the enumeration of bacteria and the isolation of pure colonies for further identification.
Image I : Pour Plate Method

Components
The Components required for the pour plate method are:
- Sample
- Sterile Petri dishes
- Sterile pipettes
- Liquefied agar medium
- Sterile water or saline solution
- Bunsen burner or hot plate
- Incubator
- Glass spreader or sterile swab
Procedure of Pour Plate Method
The procedure for this method is as follows:
- Prepare the agar medium according to the manufacturer’s instructions and sterilize it by autoclaving.
- Allow the agar to cool to approximately 45-50°C.
- Mix the sample with a sterile diluent (water or saline solution) in a test tube or flask.
- Label the Petri dishes with the necessary information, such as sample name, dilution, and date.
- Pipette 1 mL of the diluted sample onto the center of a sterile Petri dish.
- Add 9 mL of the liquefied agar medium to the Petri dish and swirl gently to mix.
- Allow the agar to solidify by keeping the Petri dishes on a level surface.
- Invert the Petri dishes and incubate them at the appropriate temperature and time for the bacterial growth.
Advantages of Pour Plate Method
The pour plate method offers several advantages over other bacterial isolation techniques, including:
- It allows the isolation of pure colonies for further identification and characterization.
- It provides a quantitative estimation of bacterial count.
- It can be used for the enumeration of viable bacteria in a sample.
- It is a simple and inexpensive method that requires minimal equipment and training.
Limitations of Pour Plate Method
The pour plate method also has some limitations, including:
- It may not be suitable for samples containing high bacterial counts as it may result in overcrowding of colonies.
- It may not be suitable for the isolation of anaerobic bacteria.
- It may be time-consuming as it requires the preparation of multiple dilutions and plates.
Quality Control of Pour Plate Method
The quality control of the pour plate method is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. The following steps can be taken for quality control:
- Use sterile materials and equipment to avoid contamination.
- Use appropriate controls, such as positive and negative controls, to verify the accuracy of the method.
- Check the agar plates for the presence of contaminants or improper growth.
- Record and analyze the data carefully to avoid errors.
Applications of Pour Plate Method
The pour plate method is widely used in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceutical industry for the detection and enumeration of bacteria in raw materials, finished products, and environmental monitoring.
- Food microbiology for the detection and enumeration of pathogens and spoilage organisms.
- Medical diagnosis for the isolation and identification of bacteria in clinical specimens.
- Environmental microbiology for the analysis of soil, water, and air samples.
Comparison with Other Techniques
The pour plate method has some advantages and disadvantages compared to other bacterial isolation techniques. For example:
- It is more reliable than the streak plate method for the isolation of pure colonies.
- It is less time-consuming than the membrane filtration method.
Troubleshooting
Some common problems that may occur during execution of This method include:
- Overcrowding of colonies due to high bacterial counts.
- Uneven distribution of bacteria in the agar medium.
- Contamination of the sample or equipment.
- Improper incubation conditions.
These problems can be prevented or resolved by proper technique, careful observation, and appropriate corrective action.
Safety Precautions
Some safety precautions to be taken during execution of this method,includes:
- Use sterile materials and equipment to avoid contamination.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and lab coat.
- Handle the sample and equipment carefully to avoid spills or splashes.
- Disinfect the work area and equipment after use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) :
What is the difference between the pour plate method and spread plate method?
- This method involves the dilution of the sample by mixing it with a sterile liquefied agar medium, whereas the spread plate method involves spreading the sample on the surface of a solid agar medium. It allows the isolation of pure colonies, while the spread plate method may result in mixed colonies.
How can I prevent contamination during the pour plate method?
- You can prevent contamination by using sterile materials and equipment, handling the sample and equipment carefully, and disinfecting the work area and equipment after use.
Can the pour plate method be used for the isolation of anaerobic bacteria?
- This method may not be suitable for the isolation of anaerobic bacteria compared to the anaerobic culture method.
What are the advantages of the pour plate method?
- It offers several advantages, including the isolation of pure colonies, quantitative estimation of bacterial count, and simplicity and affordability.
What are the limitations of the pour plate method?
- This method has some limitations, including unsuitability for high bacterial counts, unsuitability for anaerobic bacteria, and time-consuming preparation.
How do you calculate the number of viable microorganisms using the pour plate method?
- The number of viable microorganisms can be calculated by multiplying the number of colonies by the dilution factor and then dividing by the volume plated.
What factors can affect the efficiency of the pour plate method?
- The concentration of the sample, the temperature and pH of the agar medium, the volume of the sample added to the plate, the incubation time and temperature, and the type of microorganisms present in the sample can all affect the efficiency of the pour plate method.