Streak Plate Method- A Comprehensive Guide
This article contains information about streak plate method, its principle, procedure, Different types of streak plate method, Advantage, Disadvantage, Troubleshooting and Safety precautions.
What is mean by Streak Plate Method Isolation Technique ?
The streak plate method contains spreading a small amount of a mixture of microorganisms onto an agar plate and then streaking the mixture with a sterile inoculating loop in a specific pattern. The loop is then sterilized and used to streak the plate again, and the process is repeated until individual colonies of microorganisms are visible. This method is a simple, efficient, and inexpensive technique used to isolate pure cultures from mixed populations of microorganisms.
Microorganisms are ubiquitous and exist in diverse environments. It is essential to isolate and study individual microorganisms to understand their characteristics, behavior, and pathogenic potential. is is widely used isolation technique in microbiology laboratories to obtain a pure culture of microorganisms from a mixed population.
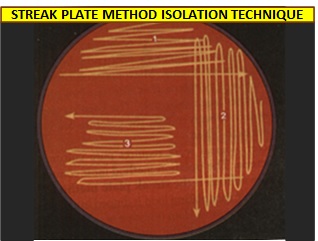
Image I : Streak Plate Methos Isolation Technique

Principles of the Streak Plate Method
The streak plate method is based on the Principle of Dilution. The mixed culture is spread over the surface of a solid agar medium in a petri dish using a loop. The loop is then sterilized and streaked again, spreading a few cells from the previous streak. This process is repeated several times, resulting in a series of dilutions, until individual cells are separated and form discrete colonies on the agar surface.
Components Required
The Components required for the streak plate method are:
- Petri dishes containing a solid agar medium
- Inoculating loop or needle
- Sterilizing equipment (Bunsen burner, autoclave, or hot air oven)
- Mixed culture sample
Procedure of Streak Plate Method
The procedure for the streak plate method is as follows:
- Sterilize the inoculating loop or needle using a Bunsen burner flame or other sterilizing equipment.
- Obtain a loopful of the mixed culture sample.
- Invert the petri dish containing the solid agar medium.
- Streak the loopful of the mixed culture on one quadrant of the agar surface.
- Sterilize the loop and streak the next quadrant, spreading a few cells from the previous streak.
- Repeat the sterilization and streaking process for the next two quadrants, resulting in four quadrants or sections.
- Incubate the petri dish upside down at an appropriate temperature for the microorganisms being tested.
Tips for Successful Streaking
To obtain a pure culture using the streak plate method, some tips are recommended:
- Use a small amount of mixed culture.
- Avoid touching the agar surface with the loop or needle.
- Flame the loop or needle before and after each streak.
- Sterilize the loop or needle until it glows red.
- Streak the first quadrant lightly and the last quadrant heavily.
- Make sure the colonies are well isolated.
Different Types of Streak Plate Method :
There are Different Types of streak plate method, Some common used methos are described below :
- Four Quadrant Streaking Method: This method involves dividing the agar plate into four quadrants and streaking each quadrant with a loopful of bacteria from the previous quadrant. This allows for the isolation of individual colonies.
- T-Streak Method: This method involves streaking the bacteria in a “T” shape on the agar plate, with each section of the “T” being streaked with bacteria from the previous section. This method is useful for separating different types of bacteria in a mixed sample.
- Zigzag Streaking Method: This method involves streaking the bacteria in a zigzag pattern across the agar plate. This is useful for obtaining a large number of colonies for further analysis.
- Dot Streaking Method: This method involves streaking the bacteria in a series of dots on the agar plate. This is useful for isolating single colonies and for counting the number of bacteria in a sample.
- The Square Method: This method involves dividing the petri dish into a grid of squares and then streaking each square with the bacteria from the previous square. This method is also used for bacterial isolation but is particularly useful when trying to obtain a high number of colonies for further analysis.
- Spiral Streaking Method: This method involves streaking the bacteria in a spiral pattern on the agar plate. This is useful for obtaining a large number of colonies and for studying the growth patterns of bacteria.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of the streak plate method are:
- It is a simple and inexpensive method.
- It allows for the isolation of pure cultures from mixed populations.
- It can be used to study the characteristics and behavior of individual microorganisms.
The disadvantages of the streak plate method are:
- It is time-consuming, as multiple streaks and incubation steps are required.
- It may not be suitable for microorganisms that require a specific environment or nutrient medium.
Applications of Streak Plate Method
The streak plate method is widely used in microbiology laboratories for various applications, such as:
- Identification of pathogenic microorganisms
- Study of microbial diversity and ecology
- Isolation of industrially useful microorganisms
- Quality control of Pharmaceutical, food and water samples
Quality Control of Streak Plate Method
To ensure the reliability and reproducibility of results obtained using the streak plate method, quality control measures should be implemented, such as:
- Use of appropriate sterilization and aseptic techniques
- Use of standardized procedures and media
- Use of reference strains and positive and negative controls
- Regular monitoring of equipment and reagents
Interpretation of Results
The results of the streak plate method should be interpreted based on the appearance and characteristics of the isolated colonies, such as:
- Colony morphology (size, shape, color, texture)
- Gram stain reaction
- Biochemical and physiological tests
Troubleshooting
If the streak plate method does not yield the expected results, some common troubleshooting steps can be followed :
- Use of a fresh culture or medium
- Adjusting the temperature, pH, or nutrient composition of the medium
- Checking for contamination or improper sterilization
- Varying the streaking pattern or inoculum size
Safety Precautions
While performing streak plate method or any other microbiological technique, some safety precautions should be taken, such as:
- Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and lab coat
- Working in a well-ventilated area
- Proper disposal of contaminated materials and waste
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of equipment and surfaces
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) :
-
What is the difference between the streak plate method and the pour plate method?
- The streak plate method involves spreading the mixed culture on the surface of the agar medium, while the pour plate method involves mixing the mixed culture with the liquid agar medium before solidification.
-
Can the streak plate method be used for anaerobic microorganisms?
- Yes, but appropriate anaerobic conditions and media should be used.
-
How long does it take to obtain pure colonies using the streak plate method?
- It depends on the growth rate and characteristics of the microorganisms being tested, but it can take several days to a week or more.
-
What is the purpose of flaming the inoculating loop or needle?
- Flaming sterilizes the loop or needle and prevents contamination.